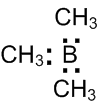Which of the following molecules acts as a Lewis acid?
-
(CH)3B
-
(CH3)O
-
(CH3)P
-
(CH3)2)O
A.
(CH)3B
According to Lewis concept " Acids are electron acceptor and bases are electron donor" Since, electron deficient compounds also have an ability to accept electrons, these are regarded as acids.
Trimethylborane (CH)3B have incomplete octet thus, act as Lewis acid.