Calculate the pOH of a solution at 250C that contains 1 x 10-10 M of hydronium ions.
-
7
-
4
-
9
-
1
B.
4
[H3O+] = [H+] = 10-10
pH + pOH = [14]
pH = - log [ H+]
pH = - log [10-10]
pH = 10
⇒ pOH + 10 = 14
⇒ pOH = 14-10 = 4
Sponsor Area
Calculate the pOH of a solution at 250C that contains 1 x 10-10 M of hydronium ions.
7
4
9
1
B.
4
[H3O+] = [H+] = 10-10
pH + pOH = [14]
pH = - log [ H+]
pH = - log [10-10]
pH = 10
⇒ pOH + 10 = 14
⇒ pOH = 14-10 = 4
Sponsor Area
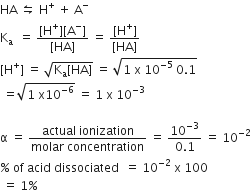
A Weak acid, HA has a Ka of 1.00 x 10-5. If 0.100 mole of this percentage of acid dissociated at equilibrium is closest to:
99.0%
1.00%
99.9 %
0.100%
B.
1.00%
Which of the following oxidation states are the most characteristics for lead and tin respectively?
+4,+2
+2,+4
+4,+4
+2,+2
B.
+2,+4
The tendency to form +2 ionic state increase on moving down the group due to the inert pair effect.
Most characteristic oxidation state for lead and tin are +2,+4 respectively.
The correct order of C-O bond length among CO, CO32-, CO2 is,
CO2< CO32-< CO
CO < CO32-< CO2
CO32- <CO2 <CO
CO < CO2 < CO32-
B.
CO < CO32-< CO2
The bond length is the average distance between the centres of nuclei of two bonded atoms. Centres of nuclei of two bonded atoms. A multiple bonds (double or triple bond) is always shorter than the corresponding single bond.
The C- atom is CO32- is sp2 hybridised as shown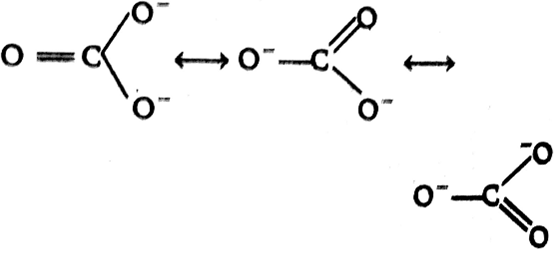
The C- atom is CO2 is sp hybridised with a bond distance of carbon -oxygen is 122 pm.
The C- atom in CO is sp hybridised with C-O bond distance is 110 pm:
So the correct order is
CO < CO32-< CO2
The following equilibrium constants are given:
N2 + 3H2 ⇌ 2NH3; K1
N2 +O2 ⇌ 2NO; K2
H2 + 1/2O2 ⇌ H2O' K3
The equilibrium constants for the oxidation of NH3 by oxygen to give NO is:
K2K33 /K1
KK2K32 /K1
K22K3 /K1
K1K2 /K3
A.
K2K33 /K1
The required equation for the oxidation of NH3 by oxygen to give NO is: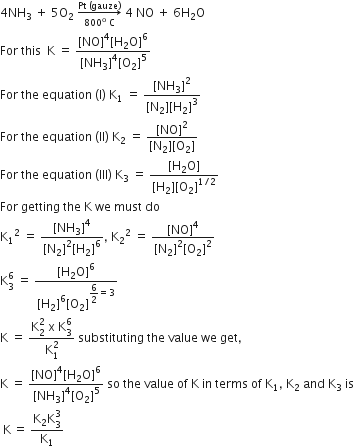
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series