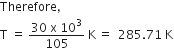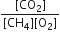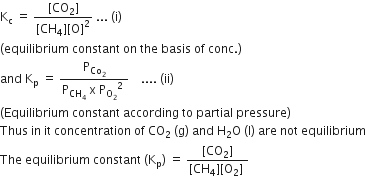Identify the correct statement for the change of Gibbs energy for a system (ΔGsystem) at constant temperature and pressure
-
If ΔGsystem > 0, the process is spontaneous
-
If ΔGsystem =0, the system has attained equilibrium
-
If ΔGsystem < 0, the system is still moving in a particular direction
-
If ΔGsystem < 0, the process is not spontaneous
B.
If ΔGsystem =0, the system has attained equilibrium
If the Gibbs free energy for a system (ΔGsystem) is equal to zero, then system is present in equilibrium at a constant temperature and pressure.