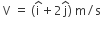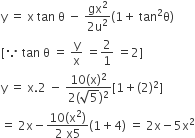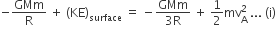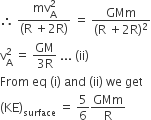This question has Statement I and Statement II. Of the four choices given after the Statements, choose the
one that best describes the two Statements.
Statement – I: A point particle of mass m moving with speed v collides with stationary point particle of mass M. If the maximum energy loss possible is given as f 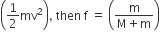
Statement – II : Maximum energy loss occurs when the particles get stuck together as a result of the collision.
-
Statement – I is true, Statement – II is true, Statement – II is a correct explanation of Statement – I.
-
Statement – I is true, Statement – II is true, Statement – II is not a correct explanation of Statement – I.
-
Statement – I is true, Statement – II is false.
-
Statement – I is false, Statement – II is true
Solution
Multi-choise Question
D.
Statement – I is false, Statement – II is true
Before collision, the mass is m and after collision, the mass is m+M
therefore, Maximum energy loss
= 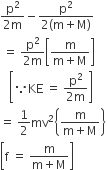
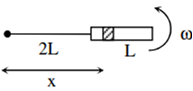
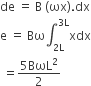



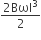
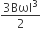
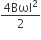



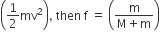
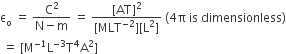
 where is along the ground and
where is along the ground and  is along the vertical. If g = 10 m/s2, the equation of its trajectory is:
is along the vertical. If g = 10 m/s2, the equation of its trajectory is: