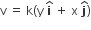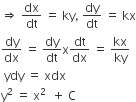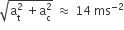STATEMENT – 1
Two particles moving in the same direction do not lose all their energy in a completely inelastic collision.
STATEMENT – 2
Principle of conservation of momentum holds true for all kinds of collisions.
-
The statement I is True, Statement II is False.
-
The statement I is True, Statement II is True; Statement II is a correct explanation for Statement I.
-
The statement I is True, Statement II is True; Statement II is not the correct explanation for Statement I.
-
Statement I is False, Statement II is
B.
The statement I is True, Statement II is True; Statement II is a correct explanation for Statement I.






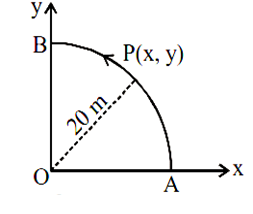
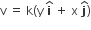 where K is a constant. The general equation for its path is
where K is a constant. The general equation for its path is