Which one of the following represents the correct dimensions of the coefficient of viscosity?
-
ML−1 T−2
-
MLT−1
-
ML−1 T−1
-
ML−2 T−2
C.
ML−1 T−1

Sponsor Area
Which one of the following represents the correct dimensions of the coefficient of viscosity?
ML−1 T−2
MLT−1
ML−1 T−1
ML−2 T−2
C.
ML−1 T−1

Sponsor Area
A particle moves in a straight line with retardation proportional to its displacement. Its loss of kinetic energy for any displacement x is proportional to
x2
ex
x
logex
A.
x2
In this problem acceleration (a) is given in terms of displacement (x) to determine the velocity with respect to position or displacement we have to apply integration method.
From given information a =-kx, where a is acceleration, x is displacement and k is proportionality constant. 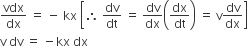
Let for any displacement from 0 to x , the velocity changes from vo to v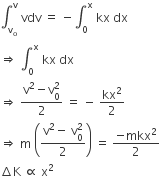
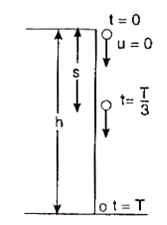
A ball is released from the top of a tower of height h metres. It takes T seconds to reach the ground. What is the position of the ball in T/3 seconds?
h/9 metres from the ground
7h/9 metres from the ground
8h/9 metres from the ground
17h/18 metres from the ground.
C.
8h/9 metres from the ground
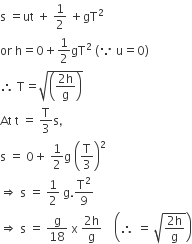
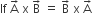 then the angle between A and B isπ
then the angle between A and B isπ
π
π/3
π/2
π/4
A.
π
A projectile can have the same range R for two angles of projection. If T1 and T2 be the time of flights in the two cases, then the product of the two time of flights is directly proportional to
1/R2
1/R
R
R2
C.
R
We know in advance that range of projectile is same for complementary angles i.e. for θ and (900 - θ )
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series