Suppose a population A has 100 observations 101, 102, … , 200, and another population B has 100 observations 151, 152, … , 250. If VA and VB represent the variances of the two populations, respectively, then VA/VB is
-
1
-
9/4
-
4/9
-
2/3
A.
1
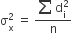 (Here deviations are taken from the mean) Since A and B both have 100 consecutive integers, therefore both have same standard deviation and hence the variance.
(Here deviations are taken from the mean) Since A and B both have 100 consecutive integers, therefore both have same standard deviation and hence the variance. 








