Let z, w be complex numbers such that z iw + = 0 and arg zw = π. Then arg z equals
-
π/4
-
5π/4
-
3π/4
-
π/2
C.
3π/4
Since z + iw = 0 ⇒ z = −iw
⇒ z = iw
⇒ w = -iz
Also arg(zw) = π
⇒ arg (-iz2) = π
⇒ arg (-i) + 2 arg(z) = π
Sponsor Area
Let z, w be complex numbers such that z iw + = 0 and arg zw = π. Then arg z equals
π/4
5π/4
3π/4
π/2
C.
3π/4
Since z + iw = 0 ⇒ z = −iw
⇒ z = iw
⇒ w = -iz
Also arg(zw) = π
⇒ arg (-iz2) = π
⇒ arg (-i) + 2 arg(z) = π
Sponsor Area
If z = x – i y and z1/3 = p+ iq , then 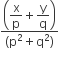 is equal to
is equal to
1
-2
2
-1
B.
-2
D.
-1
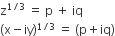 therefore,(Qz = x − iy)
therefore,(Qz = x − iy)If |z2-1|=|z|2+1, then z lies on
the real axis
an ellipse
a circle
the imaginary axis
B.
an ellipse
Given that
|z2- 1| = |z|2+ 2
|z2 + (-1)| = |z2| + |-1|
It shows that the origin, -1 and z2 lies on a line and z2 and -1 lies on one side of the origin, therefore
z2 is a negative number. Hence z will be purely imaginary. So we can say that z lies on y-axis.
If a1, a2, a3 , ....,an , .... are in G.P., then the value of the determinant  is
is
0
-2
1
2
A.
0
Let two numbers have arithmetic mean 9 and geometric mean 4. Then these numbers are the roots of the quadratic equation
x2 + 18x +16 = 0
x2-18x-16 = 0
x2+18x-16 =0
x2-18x +16 =0
D.
x2-18x +16 =0
Let α and β be two numbers whose arithmetic mean is 9 and geometric mean is 4.
∴ α + β = 18 ........... (i)
and αβ =16 ........... (ii)
∴ Required equation is x2 - (α + β)x + (αβ) = 0 ⇒ x2 - 18x + 16 = 0 [using equation (i) and equation (ii)]
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series