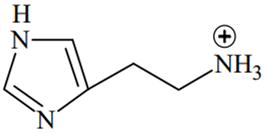
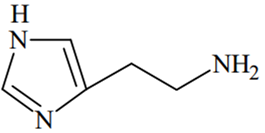
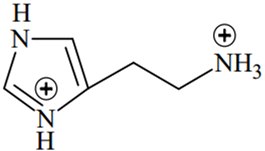
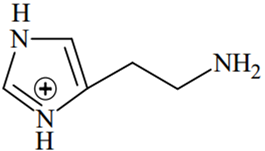
An alkali is titrated against an acid with methyl orange as indicator, which of the following is a correct combination?
Base Acid End Point Strong Strong Pink to colourless Base Acid End Point Weak Strong Colourless to pink Base Acid End Point Strong Strong Pinkish Red to Yellow Base Acid End Point Weak Strong Yellow to Pinkish Red
D.
| Base | Acid | End Point |
| Weak | Strong | Yellow to Pinkish Red |
Methyl orange is the weak organic base. It is used in the titration of WB vs SA
In a basic medium, equilibrium lies in the backward direction and therefore it shows yellow colour.
In acidic medium, equilibrium shifts in forwarding direction and therefore, colour changes from yellow to red.