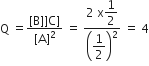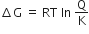The molecular formula of a commercial resin used for exchanging ions in water softening is C8H7SO3Na ( mol. wt = 206). What would be the maximum uptake of Ca2+ ions by the resin when expressed in mole per gram resin?
-
1/103
-
1/206
-
2/309
-
1/412
D.
1/412
We know the molecular weight of C8H7SO3Na
= 12x8+1x7+32+16x3+23 = 206
we have to find mole per gram of resin
therefore,
1 g of C8H7SO3Na has number of mole
=1/206 mol
Taking the reaction,
C8H7SO3Na + Ca2+ → (C6H7SO3)2Ca + 2Na+
therefore, 2 moles of C8H7SO3Na combines with 1 mol of Ca2+
Thus, 1 mole of C8H7SO3Na will combine with 0.5 mol of Ca2+
Hence, 1/206 mole of C8H7SO3Na will combine with,
0.5 x (1/206)mol of Ca2+ = 1/412 mol Ca2+






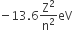
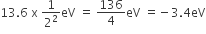
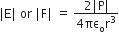
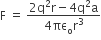
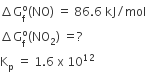
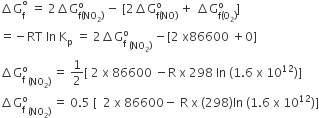
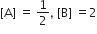 and
and 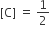 , The reaction proceeds in the [R= 8.314 JK/mol, e = 2.718]
, The reaction proceeds in the [R= 8.314 JK/mol, e = 2.718]