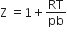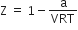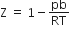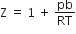The correct set of four quantum numbers for the valence electrons fo rubidium atom (Z = 37) is
-
5,0,0, +1/2
-
5,1,0,6+1/2
-
5,1,1,+1/2
-
5,0,1,+1/2
A.
5,0,0, +1/2
the atomic number of Rb (Z) = 37
Thus, its electronic configuration [Kr]5s1. since the last electron or valence electron enters in 5s subshell. So, the quantum numbers are n = 5, l =0(for s orbital) m=0
(m = +l to -l), s = +1/2 or -1/2