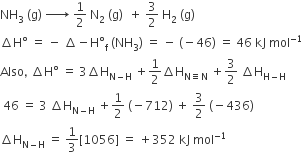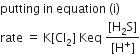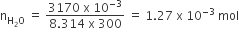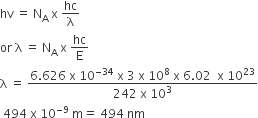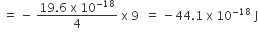The standard enthalpy of formation of NH3 is– 46.0 kJmol–1. If the enthalpy of formation of H2 from its atoms is – 436 kJ mol–1 and that of N2 is – 712 kJ mol–1,the average bond enthalpy of N – H bond is NH3 is
-
-964 kJ mol-1
-
+352 kJ mol-1
-
+1056 kJ mol-1
-
-1102 kJ mol-1
B.
+352 kJ mol-1