ICSE physics
Sponsor Area
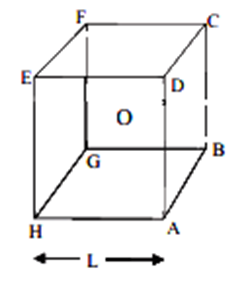
A short electric dipole (consists of two point charges +q and -q) is placed at the centre O and inside a large cube (ABCDEFGH) of length L, as shown in the figure below. The electric flux, remaining through the cube is:
-

-
Zero
-

-

B.
Zero
Since, it is an electric dipole, the net charge enclosed by the surface is zero. Therefore, according to Gauss's law, electric flux through the cube will be zero.
Sponsor Area
The equivalent resistance between points a and f of the network as shown in the figure below is:

-
24 ohm
-
110 ohm
-
140 ohm
-
200 ohm
C.
140 ohm
A moving electron enters a uniform and perpendicular magnetic field. Inside the magnetic field, the electrons travels along,
-
a straight line
-
a parabola
-
a circle
-
a hyperbola
C.
a circle
A fish which is at a depth of 12 cm in water ( ) is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. It's apparent depth as observed by the observer is:
) is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. It's apparent depth as observed by the observer is:
-
3 cm
-
9 cm
-
12 cm
-
16 cm
B.
9 cm
Given,
Real depth of fish = 12 cm
Refractive Index = 4/3
Using the formula,
If EP and EK represent potential energy and kinetic energy respectively, of an orbital electron, then according to the Bohr's theory:
-
Ek = -EP/2
-
Ek = -EP
-
Ek = -2EP
-
Ek = 2 EP
A.
Ek = -EP/2
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





