A ray of light is moving from a rarer medium to a denser medium and strikes a plane mirror placed at 90o to the direction of the ray as shown in the diagram.
i) Copy the diagram and mark arrows to show the path of the ray of light after it is reflected from the mirror.
ii) Name the principle you have used to mark the arrow to show the direction of the ray.
i) The direction of the ray of light is as shown below: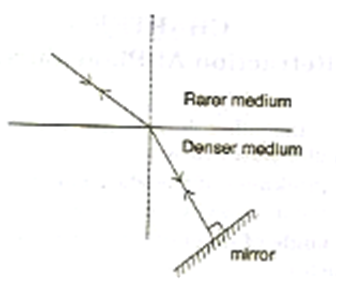
ii) The principle of reversibility of light.







 ; Real depth = ?
; Real depth = ?




