ICSE physics
Sponsor Area
A body of mass 1.50 kg is dropped from the second floor of a building which is at a height of 12 m. What is the force acting on it during its fall? ( g = 9.8 m/s2)
Using the formula,
F = mg
= 1.5 x 9.8
= 14.7 N
Sponsor Area
When an arrow is shot from a bow, it has kinetic energy in it. Explain briefly from where does it get its kinetic Energy?
When bow is stretched, work is done on it which has elastic potential energy and on releasing it, potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
What energy conversion take place in the following when they are working:
i) Electricity toaster
ii) Microphone
i) Electric Energy to heat energy.
ii) Sound energy to electrical energy.
In what way will the temperature of water at the bottom of a waterfall be different from the temperature at the top? Give a reason for your answer.
Temperature at the bottom is more, because the potential energy at top converts to heat energy when water reaches at bottom, as a result temperature of water at the bottom increases.
i) A stone of mass 64.0 g is thrown vertically upward from the ground with an initial speed of 20.0 m/s. The gravitational potential energy at a group level is considered to be zero. Apply the principle of conservation of energy and calculate the potential energy at the maximum height attained by the stone. (g = 10 m/s2)
ii) Using the same principle, state what will be the total energy of the body at its half-way point?
i)
Given:
Mass of the stone, m = 64.0 g;
Initial speed with which the stone is thrown, v = 20 m/s
Potential energy at top = K.E at ground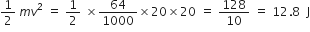
ii) Total energy of the stone would remain the same. i.e., 12.8 J
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





