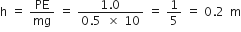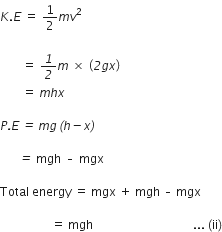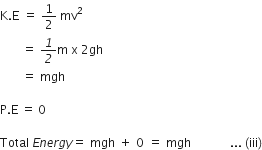Show that for the free fall of a body, the sum of the mechanical energy at any point in its path is constant.
Let a body of mass m fall freely under gravity from height h above ground.
Let, A B and C be the positions of body.
Let x be the distance fallen from A to B.
At position A:
K.E= 0 (body is at rest)
P.E = mgh
Therefore,
Total energy = 0 + mgh = mgh … (i)
At position B:
Let v1 be velocity of body, then u = 0
S= x
Using equation of motion, we have
V2 = u2 + 2as
V12 = 0 + 2 gx
V12 = 2 gx
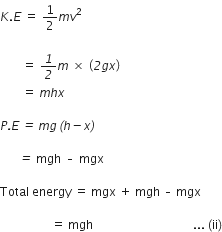
At position C:
Let velocity of body be v.
Then, u = 0 and S = h
From equation,
V2 = u2 + 2gs
V2 = 0 + 2gh
V2 = 2gh
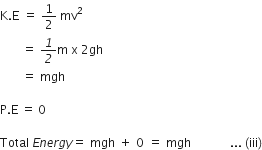
Therefore, from equations (i), (ii) and (iii), it is clear that the sum of mechanical energy remains same at any point in the path of free fall of a body.