CBSE physics
Sponsor Area
Define the term 'Mobility' of charge carriers in a conductor. Write its S.I. unit
Drift velocity per unit applied electric field is known as the mobility of charge carriers in a conductor.
Mathematically,
Mobility, 
S.I. unit of mobility: 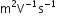 or
or 
Sponsor Area
The carrier wave is given by C (t) = 2sin (8πt) Volt.
The modulating signal is a square wave as shown. Find modulation index. 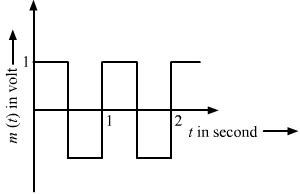
The generalized equation of a carrier wave is given by, 
The generalized equation of a modulating signal is given by,
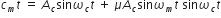
On comparing the given equation of carrier wave with the generalized equation, we get,
Amplitude of modulating signal, Am = 1 V
Amplitude of carrier wave, Ac = 2 V
Modulation index is the ratio of the amplitude of modulating signal to the amplitude of carrier wave 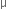 .
.
It is denoted by,
So, 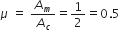
"For any charge configuration, equipotential surface through a point is normal to the electric field." Justify.
Work done (W) in moving a test charge along an equipotential surface is zero.
Work done is given by, 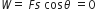
F is the electric force and s is the magnitude of displacement.
For non-zero displacement, this is possible only when cos  is equal to 0.
is equal to 0.
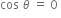
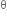 = 90°
= 90°
Thus, the force acting on the point charge is perpendicular to the equipotential surface.
Electric field lines give us the direction of electric force on a charge.
Thus, for any charge configuration, equipotential surface through a point is normal to the electric field.
Two spherical bobs, one metallic and the other of glass, of the same size are allowed to fall freely from the same height above the ground. Which of the two would reach earlier and why?
The glass bob would reach the ground earlier. Glass bob which is non-conducting in nature will only experience Earth’s gravitational pull unlike the metallic bob which is conducting.
Since the metallic bob is conducting in nature, eddy current is induced as it falls through the magnetic field of the Earth. As per Lenz’s law, current is induced in a direction opposite to the motion of the metallic bob. Hence, there is a delay.
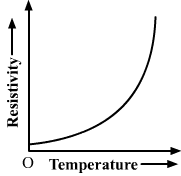
Show variation of resistivity of copper as a function of temperature in a graph.
The graph below shows variation of resistivity of copper with temperature. The graph is parabolic in nature.
'
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





