CBSE chemistry
Sponsor Area
‘Crystalline solids are anisotropic in nature’. What does this statement mean?
All crystalline solids are not anisotropic. Those crystalline solids which are anisotropic have their atoms arranged and spaced in a different manner in three different planes (X, Y and Z). Therefore, the physical properties of crystalline solids such as electrical resistance or refractive index show different values when measured along different directions in the same crystals.
Example NaCl, Quartz, Ice, HCl, Iron, etc.
Sponsor Area
Express the relation between conductivity and molar conductivity of a solution held in a cell.
The molar conductivity of a solution at a given concentration is the conductance of volume V of a solution containing 1 mole of the electrolyte kept between two electrodes with the area of cross-section A and distance of unit length, the conductivity of the solution is given by the following relation.

Define electrophoresis ?
1. The migration of charged colloidal particles or molecules through a solution under the influence of an applied electric field usually provided by immersed electrodes. Also called ionophoresis, phoresis.
2. A method of separating substances, especially proteins, and analyzing molecular structure based on the rate of movement of each component in a colloidal suspension while under the influence of an electric field.
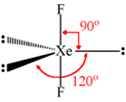
Draw the structure of XeF2 molecule.
The chemistry of corrosion of iron is essentially an electrochemical phenomenon. Explain the reactions occurring during the corrosion of iron in the atmosphere.
The process of corrosion is a redox reaction and involves simultaneous oxidation and reduction reactions. It can, therefore, be referred to as an electrochemical reaction.
In the process of corrosion, due to the presence of air and moisture, oxidation takes place at a particular spot of an object made of iron. That spot behaves as the anode. The reaction at the anode is can be written as follows.
Anode reaction: ![]()
Electrons released at the anodic spot move through the metallic object and go to another spot of the object. There, in the presence of H+ ions, the electrons reduce molecular oxygen. This spot behaves as the cathode. These H+ ions come either from H2CO3, which are formed due to the dissolution of carbon dioxide from the air into water or from the dissolution of other acidic oxides from the atmosphere in water.
The reaction corresponding at the cathode is written as follows.
Cathode reaction:
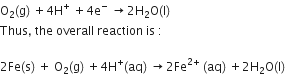
Also, ferrous ions are further oxidised by atmospheric oxygen to ferric ions.
These ferric ions combine with moisture, present in the surroundings, to form a hydrated ferric oxide (Fe2O3, x H2O) i.e., rust.
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





