CBSE science
Sponsor Area
The atomic numbers of three elements A, B and C are 12, 18 and 20 respectively. State, giving a reason, which two elements will show similar properties.
The elements are,
A-(Atomic number 12) = Magnesium
B-(Atomic number 18) = Argon
C-(Atomic number 20) = Calcium
Element Calcium and magnesium will show similar properties as they belong to the same group (Group II) of the periodic table. They have the same number of valence electrons and they both are metals. While argon is a noble gas.
Sponsor Area
Study the following table in which positions of six elements A, B, C, D, E and F are shown as they are in the modern periodic table: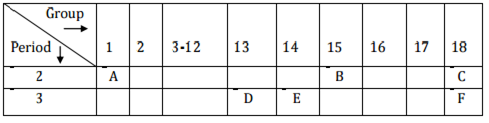
On the basis of the above table, answer the following questions:
(i) Name the element which forms only covalent compounds.
(ii) Name the element which is a metal with valency three.
(iii) Name the element which is a non-metal with valency three.
(iv) Out of D and E, which is bigger in size and why?
(v) Write the common name for the family to which the elements C and F belong.
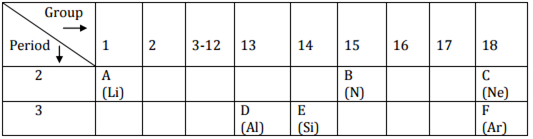
(i) Element E - Silicon forms only covalent compounds.
(ii) Aluminium is a metal with the valency 3.
(iii) Nitrogen is a nonmetal with the valency 3.
(iv) Out of D (Aluminium) and E (Silicon), aluminium has a larger size than silicon.
This is because atomic size decreases across the period.
(v) Common name for the family to which the elements C (Neon) and F (Argon)
belong is 'Noble gas' or 'Inert gas'.
The elements Be, Mg and Ca each having two electrons in their outermost shells are in periods 2, 3, and 4 respectively of the modern periodic table. Answer the following questions, giving justification in each case:
(i) Write the group to which these elements belong.
(ii) Name the least reactive element.
(iii) Name the element having a largest atomic radius.
(i) Elements Be, Mg and Ca belong to Group II.
(ii) Beryllium (Be) is the least reactive element. This is because, as we move down the group, the number of shells increases and the effective nuclear charge decreases. Thus, the tendency to lose electrons increases.
(iii) Calcium has the largest atomic radius. Since, the number of shells increases down the group atomic radius also increases.
A carboxylic acid (molecular formula C2H402) reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to form a compound 'X'. The alcohol on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 followed by acidification gives the same carboxylic acid C2H402. Write the name and structure of
(i) carboxylic acid, (ii) alcohol and (iii) the compound 'X'.
The chemical name of given carboxylic acid is ethanoic acid. When ethanoic acid reacts with the acid in the presence of an acid such as sulphuric acid as a catalyst to produce the ester, (ethyl ethanoate).
i) Carboxylic acid = Ethanoic acid
ii) alcohol = Ethyl alcohol
iii) Compound X = ethyl ethanoate
Define the term ‘structural’ isomerism'. Explain why propane cannot exhibit this property. Draw the structures of possible isomers of butane, C4H10 .
Structural isomerism can be defined as a carbon compound which has same molecular formula but different structural formula.
Propane has the chemical formula C3H8 and it is represented as CH3-CH2-CH3. In alkanes, isomerism arises when a particular compound can be represented in the form of both straight chain and branched chain. Also, the branching cannot be done from the first or the last carbon atom of the structure.
The structural formulae of propane show that they do not have a sufficient number of carbon atoms to exist in the form of branched isomer. Hence, they do not exhibit structural isomerism.
Isomers of Butane: There are two isomers. N-butane and iso-butane.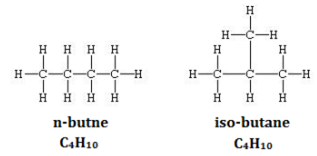
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





