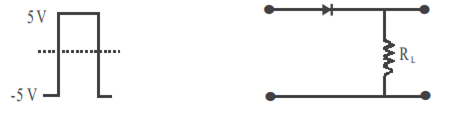
A student wants to use two p-n junction diodes to convert alternating current into direct current. Draw the labelled circuit diagram she would use and explain how it works.
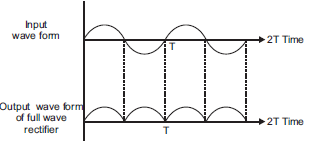
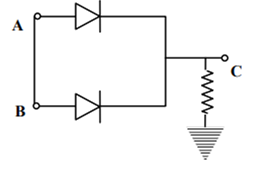
The circuit of full wave rectifier is as shown below;
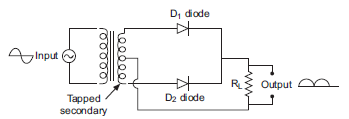
Principle: The underlying working principle of full wave rectifier is that the p-n junction conducts when it is forward biased and does not condut when it is reverse biased.