Study the diagram and answer the following questions: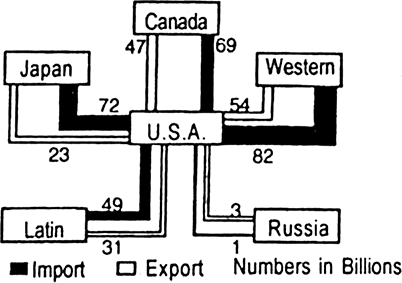
A. Name the country with which both the import and export of the U.S.A. are lowest.
B. How much is the total value of trade of the U.S.A. with Western Europe ?
C. How much is the value of imports of the U.S.A. from Japan?
D. What is the balance of trade of the U.S.A with Canada?
A. Russia
B. 13.6 billion dollar
C. 72 billion dollar
D. It is unfavourable.





