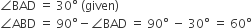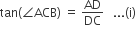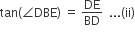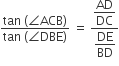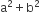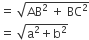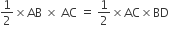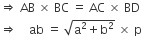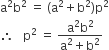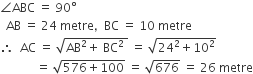are three angles of a triangle, If
are three angles of a triangle, If 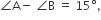
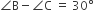 , then
, then are
are
-
80°, 60°, 40°
-
70°, 50°, 60°
-
80°, 65°, 35°
-
80°, 55°, 45°
80°, 60°, 40°
70°, 50°, 60°
80°, 65°, 35°
80°, 55°, 45°
C.
80°, 65°, 35°
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° ...(i)
(∠B - ∠C) - (∠A - ∠B ) = 30° - 15°
⟹ 2∠B - ∠A - ∠C = 15° ...(ii)
By adding (i) and (ii),
3∠B = 180° + 15° = 195°
⟹ ∠B = 65°
∠A - ∠B = 15°
⟹ ∠A = 15° + 65° = 80°
∠C = ∠B - 30°
= 65° - 30° = 35°






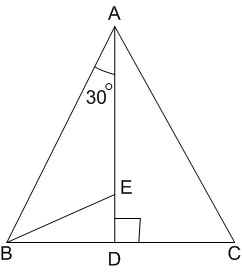
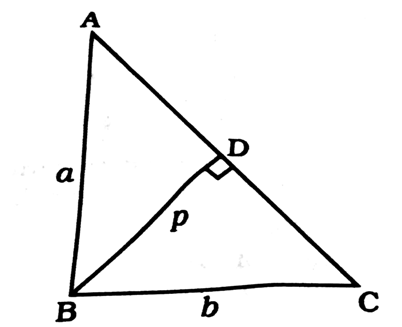
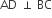 . E is a point on AD for which AE : ED = 5 : 1. If
. E is a point on AD for which AE : ED = 5 : 1. If  and then
and then 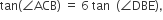 then
then