Thermodynamics
Sponsor Area
4.0 g of a gas occupies 22.4 L at NTP. The specific heat capacity of the gas at constant volume is 5.0 JK-1 mol-1. If the speed of sound in this gas at NTP is 952 ms-1, then the heat capacity at constant pressure is.
(Take gas constant R = 8.3 Jk-1 mol-1)
-
8.0 JK-1mol-1
-
7.5 JK-1mol-1
-
7.0 JK-1mol-1
-
8.5 JK-1mol-1
A.
8.0 JK-1mol-1
Given, M = 4 gm
V= 22.4 L,
CV = 5 JK-1 mol-1
Sponsor Area
A Carnot engine whose sink is at 300 K has an efficiency of 40%. By how much should the temperature of source be increased so as to increase its efficiency by 50% of original efficiency?
-
275 K
-
175 K
-
250 K
-
225 K
C.
250 K
The efficiency of Carnot engine is defined as the ratio of work done to the heat supplied i.e.,
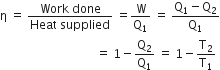
Here,  is the temperature of source and T2 is the temperature of sink
is the temperature of source and T2 is the temperature of sink
As given, 
and 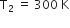
So,

Let temperature of the source be increased by x K, then efficiency becomes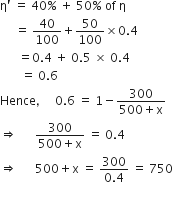

A Carnot engine, having an efficiency of as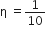 heat engine, is used as a refrigerator. If the work is done on the system is 10J, the amount of energy absorbed from the reservoir at lower temperature is
heat engine, is used as a refrigerator. If the work is done on the system is 10J, the amount of energy absorbed from the reservoir at lower temperature is
-
100J
-
99 J
-
90 J
-
1 J
C.
90 J
According to Carnot engine,
As Q1 +W = Q2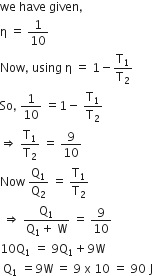
A gas is compressed isothermally to half its initial volume. The same gas is compressed separately through an adiabatic process until its volume is again reduced its half. Then,
-
compressing the gas through adiabatic process will require more work to b done
-
compressing the gas through isothermally or adiabatically will require the same amount of work.
-
which of the case (whether compression through isohermal or through adiabatic process) requires more work will depend upon the atomicity of the gas.
-
compressing the gas isothermally will require more work to be done
B.
compressing the gas through isothermally or adiabatically will require the same amount of work.
Plotting P-V graph for the compression of a gas isothermally and adiabatically simultaneously to half of its initial volume.
 An isothermal curve is less steeper than the adiabatic curve. So, area under the P-V curve for adiabatic process has more magnitude than the isothermal curve. Hence, work done in adiabatic process will be more than in isothermal process.
An isothermal curve is less steeper than the adiabatic curve. So, area under the P-V curve for adiabatic process has more magnitude than the isothermal curve. Hence, work done in adiabatic process will be more than in isothermal process.A gas is taken through the cycle A → B → C → A, as shown, What is the net work done by the gas?
-
2000 J
-
1000 J
-
Zero
-
-2000 J
B.
1000 J
Net work done = Area enclosed in pV curve i.e. Δ ABC
= 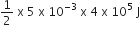 = 1000 J
= 1000 J
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





