Kinetic Theory
Sponsor Area
A particle of mass M starting from rest undergoes uniform acceleration. If the speed acquired in time T is v, the power delivered to the particle is
-
Mv2/T
-
Mv2 / 2T2
-
Mv2/T2
-
Mv2 / 2T
D.
Mv2 / 2T
The kinetic energy of particle = Mv2 / 2
Power = Energy /Time
P = Mv2 /2T
Sponsor Area
An engine pumps water continuously through a hose. Water leaves the hose with a velocity v and m is the mass per unit length of the water jet. What is the rate at which kinetic energy is imparted to water?
-
mv3 /2
-
mv3
-
mv2/2
-
m2v2 /2
A.
mv3 /2
Let m is the mass per unit length rate of mass per sec = mx/t = mv
Rate of KE = (mv)v2/2 = mv3/2
At 10o C the value of the density of a fixed mass of an ideal gas divided by its pressure is x. At 110o C this ratio is
-
x
-
383x/283
-
10x/110
-
283x/383
D.
283x/383
Writing ideal gas law
PV = nRT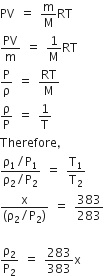
In producing chlorine by electrolysis 100 kW power at 125 V is being consumed. How much chlorine per minute is liberated (ECE of chlorine is 0.367 x 10-6 KgC-1)
-
1.76 x 10-3 kg
-
9.67 x 10-3 kg
-
17.61 x 10-3 kg
-
3.67 x 10-3 kg
C.
17.61 x 10-3 kg
Mass of the substance deposited at the cathode
m= zit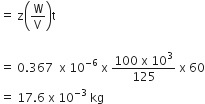
In the given (V-T )diagram, what is the relation between pressures p1 and p2?
-
p2 =p1
-
p2>p1
-
p2<p1
-
Cannot be predicted
C.
p2<p1
The slope of the graph directly proportional to 1/p
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





