If the lattice parameter for a crystalline structure is 3.6 A, then atomic radius in fcc crystal is
-
1.18 A
-
2.10 A
-
2.92 A
-
1.27 A
D.
1.27 A
Atomic radius is the distance between two nearest neighbours. For Fcc crystal 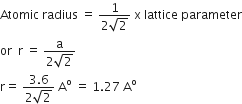
Sponsor Area
If the lattice parameter for a crystalline structure is 3.6 A, then atomic radius in fcc crystal is
1.18 A
2.10 A
2.92 A
1.27 A
D.
1.27 A
Atomic radius is the distance between two nearest neighbours. For Fcc crystal 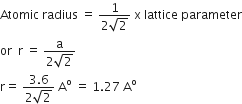
Sponsor Area
Which one of the following bonds produces a solid that reflects light in the visible region and whose electrical conductivity decreases with temperature and hs high melting point?
metallic bonding
van der Waal's bonding
Ionic bonding
covalent bonding
A.
metallic bonding
Metallic bonding is formed due to the attraction of valence (free) electrons with the positive ion cores. Their conductivity decreases with rising of temperature. When visible light falls on a metallic crystal, the electrons of atoms absorb visible light, so they are opaque to visible light. However, some orbital electrons absorb energy and reach to an excited state. They then return to their normal state, remitting light of the same frequency.
Assertion: Unlike electric force and gravitational forces, nuclear force has limited range.
Reason: Nuclear force do not obey inverse square law.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Gravitational force:- Weakest force, but infinite range ( not part of standard model)
Weak Nuclear Force:- Next weakest, but short range
Electromagnetic Force:- Stronger, with infinite range
Strong Nuclear force:- strongest, but short range
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series