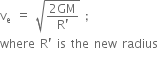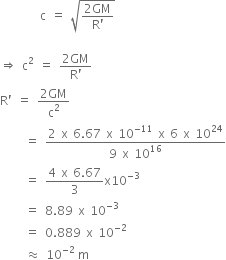(1) Centre a gravity (CG) of a body is the point at which the weight of the body acts.
(2) Centre of mass coincides with the centre of gravity if the earth is assumed to have infinitely large radius
(3) To evaluate the gravitational field intensity due to anybody can be considered to be concentrated at its CG.
(4) The radius of gyration of anybody rotating about an axis is the length of the perpendicular dropped from the CG of the body to the axis.
Which one of the following pairs of statements is correct?
-
(4) and (1)
-
(1) and (2)
-
(2) and (3)
-
(3) and (4)
A.
(4) and (1)
Centre of gravity of a body is the point at which the weight of the body acts and the radius of gyration of any body rotating about an axis is the length of the perpendicular dropped from the CG of the body to the axis.