Current Electricity
Sponsor Area
A cell having an emf and internal resistance r is connected across a variable external resistance R. As the resistance R is increased, the plot of potential difference V across R is given by
C.

Here, E = I (R+r)
E = IR+I
and
E= V+Ir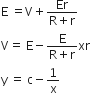
This equation represents option (c).
Sponsor Area
A circuit contains an ammeter, a battery of 30 V and a resistance 40.8 Ω all connected in series. If the ammeter has a coil of resistance 480 Ω and a shunt 20 Ω then reading in the ammeter will be
-
0.5 A
-
0.25 A
-
2 A
-
1 A
A.
0.5 A
Eeffective resistance of a circuit, 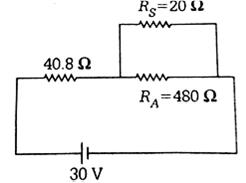

A current of 3 A flows through the 2 Ω resistor shown in the circuit. The power dissiated in the 5 Ω resistor is
diagram
-
4 W
-
2 W
-
1 W
-
5 W
D.
5 W
Voltage across 2 Ω is same as voltage across arm containing 1 Ω and 5 Ω resistance.
Voltage across 2 Ω resistance,
V = 2 x 3 = 6 V
So, voltage across lowest arm,
V1 = 6 V
Current across 5 Ω, I = 6/ 1+6 = 1 A
Thus, power across 5 Ω,
P = I2R = (1)2 x 5 = 5 W
A current 2 A flows through a 2 Ω resistor when connected across a battery. The same battery supplies a current of 0.5 A when connected across a 9 Ω resistor. The internal resistance of the battery is
-
1/3 Ω
-
1/4 Ω
-
1 Ω
-
0.5 Ω
A.
1/3 Ω
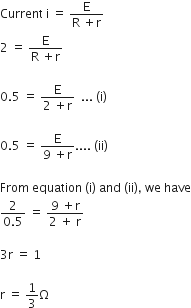
A millivoltmeter of 25 mV range is to be converted into an ammeter of 25 A range. The value (in ohm) of necessary shunt will be
-
0.001
-
0.01
-
1
-
0.05
A.
0.001
The full-scale deflection current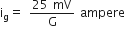
Where G is the resistance of the meter. The value of shunt required for converting it into ammeter of range 25 A is 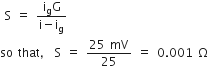
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series








