Aldehydes, Ketones And Carboxylic Acids
Sponsor Area
A carbonyl compound reacts with hydrogen cyanide to form cyanohydrin which on hydrolysis forms a racemic mixture of alpha -hydroxy acid. The carbonyl compound is:
-
CH3-CH2-CH2COCH3
-
(CH3)2C=O
-
CH3CH2CHO
-
CH3CHO
D.
CH3CHO
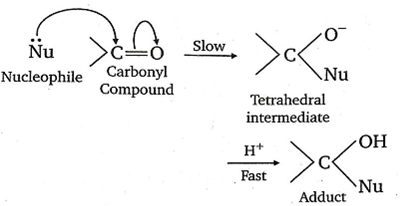
The carbonyl compounds undergo nucleophilic addition reaction because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon. As such, it withdraws share pi electron pair towards itself and gets a partial negative charge, therefore carbon gets a partial positive charge and becomes susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
The aldehyde is more reactive than ketones towards nucleophiles. This can be explained on the basis of inductive effect as well as steric effect. The addition of nucleophiles is based upon the positive charge present on a carbon atom of > C =O group.
In aldehyde >C=O group is present at least one alkyl group (except formaldehyde) which has +I effect (electron donating effect) and which decreases the positive charge of carbon, thereby making the attack to nucleophile difficult. The nucleophilic attack becomes more difficult in ketones having a minimum of two alkyl groups.
Hence, by means of attachment of alkyl groups (due to +I effect) rate of nucleophiles addition decreases.
Order of +I effect in an alkyl group.![]()
order of nucleophilic addition in given carbonyl compound is
CH3CHO > CH3-CH2- CHO > (CH3)2CO> CH3CH2CH2COCH3
Sponsor Area
A carbonyl compound reacts with hydrogen cyanide to form cyanohydrin which on hydrolysis forms a racemic mixture of alpha-hydroxy acid. The carbonyl compound is:
-
acetaldehyde
-
acetone
-
diethyl ketone
-
formaldehyde
A.
acetaldehyde
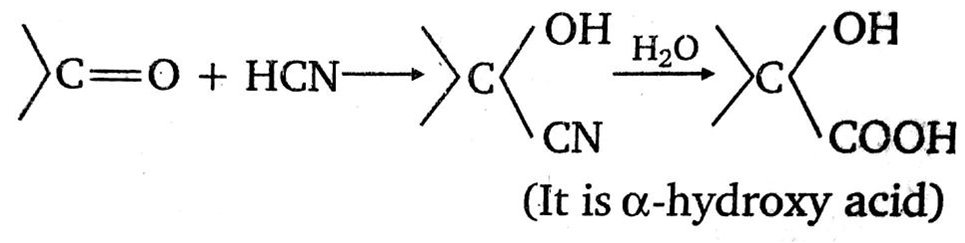
If it is a racemic mixture, therefore such 'C' atom must be the asymmetric carbon atom.

A organic compound 'A' on treatment with NH3 gives 'B' which on heating gives 'C', 'C" when treated with Br2 in the presence of KOH produces ethylamine. Compound ' A' is
-
CH3COOH
-
CH3CH2CH2COOH
-
CH3(CH3)CHCOOH
-
CH3CH2COOH
D.
CH3CH2COOH


A reaction of a carbonyl compound with one of the following reagents involves nucleophilic addition followed by the elimination of water. The reagents is
-
a Grignard reagent
-
hydrazine in presence of feebly acidic solution
-
hydrocyanic acid
-
sodium hydrogen sulphite
C.
hydrocyanic acid
Reaction of carbonyl compounds with ammonia derivatives give addition product followed by the elimination reaction. Slightly acidic medium generate a nucleophilic centre for the attack of weak base like ammonia derivatives.
Acetamide is treated with the following reagents separately. Which one of these would yield methylamine?
-
NaOH - Br2
-
Sodalime
-
Hot conc. H2SO4
-
PCl5
A.
NaOH - Br2
The reagent which can convert -CONH2 group into - NH2 group is used for this reaction.
Among the given reagents only NaOH/ Br2 converts -CONH2 group to -NH2 group, thus it is used for converting acetamide to methylamine. This reaction is called Hoffman bromide reaction.
CH3CONH2 + NaOH +Br2 --> CH3NH2 +NaBr + Na2CO3 + H2O
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





