Structure Of Atom
Sponsor Area
A 0.66 kg ball is moving with a speed of 100 m/s. The associated wavelength will be
(h = 6.6 x 10-34 Js)
-
6.6 x 10-32 m
-
6.6 x 10-34 m
-
1 x 10-35 m
-
1 x 10-32
C.
1 x 10-35 m
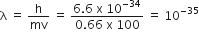
Sponsor Area
According to the Bohr theory, which of the following transitions in the hydrogen atom will give rise to the least energetic photon?
-
n= 6 to n = 1
-
n = 5 to n = 4
-
n= 6 to n = 5
-
n = 5 to n = 3
C.
n= 6 to n = 5
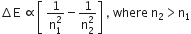
Energy of photon obtained from the transition n = 6 to n = 5 will have least energy.
Based on equation
E=-2.178 x 10-18 J  certain conclusions are written. Which of them is not correct?
certain conclusions are written. Which of them is not correct?
-
The negative sign in the equation simply means that the energy of an electron bound to the nucleus is lower than if would be if the electrons were at the infinite distance from the nucleus.
-
Larger the value of n, the larger is the orbit radius
-
Equation can be used to calculate the change in energy when the electron changes orbit
-
For n=1 the electron has a more negative energy than it does for n=6 which means that the electron is more loosely bound in the smallest allowed orbit.
D.
For n=1 the electron has a more negative energy than it does for n=6 which means that the electron is more loosely bound in the smallest allowed orbit.
If n=1,
E1 = - 2.178 x 10-18 Z2 J
If n=6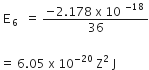
From the above calculation, it is obvious that electron has a more negative energy than it does for n=6. it means that electron is more strongly bound in the smallest allowed orbit.
Calculate the energy in joule corresponding to light of wavelength 45mm: (Planck's constant h=6.63 x10-34)Js; speed of light c= 3 x 108 ms-1)
-
6.67 x 1015
-
6.67 x 1011
-
4.42 x 10-15
-
4.42 x 10-18
D.
4.42 x 10-18
The wavelength of light is related to its energy by the equation,

Given: The mass of electron is 9.11 x 10-31 kg
Planck constant is 6.626 x 10-34 Js,
the uncertainty involved in the measurement of velocity within a distance of 0.1 A is:
-
5.79 x 106 ms-1
-
5.79 x 107 ms-1
-
5.79 x 108 ms-1
-
5.79 x 105 ms-1
A.
5.79 x 106 ms-1
By Heisenberg's uncertainty principle
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





