0.5 Molal aqueous solution of aweak acid (HX) is 20% ionised. If Kf for water is1.86 K kg mol-1, the lowering in freezing point of the solution is:
-
-1.12 K
-
0.56 K
-
1.12 K
-
-0.56 K
C.
1.12 K
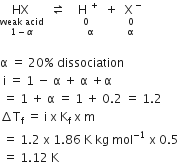
Sponsor Area
0.5 Molal aqueous solution of aweak acid (HX) is 20% ionised. If Kf for water is1.86 K kg mol-1, the lowering in freezing point of the solution is:
-1.12 K
0.56 K
1.12 K
-0.56 K
C.
1.12 K
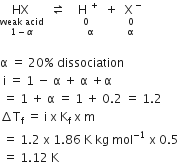
Sponsor Area
1.00 g of a non- electrolyte solute (molar mass 250 g mol-1) was dissolved in 51.2 g of benzene. If the freezing point depression constant, Kf of benzene is 5.12 K Kg mol-1, the freezing point of benzene will be lowered by:
0.4 K
0.3 K
0.5 K
0.2 K
A.
0.4 K
Molality of non- electrolyte solute
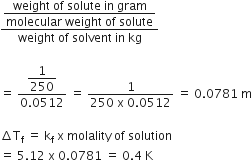
200 mL of an aqueous solution of a protein contains its 1.26 g . The osmotic pressure of this solution at 300 K is found to be 2.57 x 10-3 bar. The molar mass of protein will be (R = 0.083 L bar mol-1 K-1)
51022 g mol-1
122044 g mol-1
31011 g mol-1
61038 g mol-1
D.
61038 g mol-1
25.3 g of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3 is dissolved in enough water to make 250 mL of solution. If sodium carbonate dissociates completely molar concentration of sodium ion, Na+ and carbonate ion, CO32- are respectively (Molar mass of Na2CO3 = 106 g mol-1)
0.955 M and 1.910 M
1.910 M and 0.955 M
1.90 M and 1.910 M
0.477 M and 0.477 M
B.
1.910 M and 0.955 M
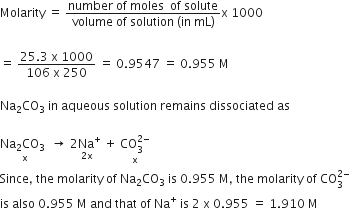
A 0.0020 m aqueous solution of an ionic compound Co(NH3)5(NO2)Cl freezes at -0.00732o C . Number of moles of ions which 1 mol of ionic compound produces on being dissolved in water will be (kf = - 1.86o C/m)
2
3
4
1
A.
2
Given,
molality = 0.0020 m
Δ Tf = 0o C -0.007320 C
kf = 1.86 oC/m
ΔTf = i.kf x m
i = ΔTf/ kf x m
= 0.00732/1.82 x 0.0020
= 1.92 = 2
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series