Equilibrium
Sponsor Area
A buffer solution is prepared in which the concentration of NH3 is 0.30 M and the concentration of NH4 is 0.20 M. If the equilibrium constant, Kb for NH3 equals 1.8 x 10-5, what is the pH of this solution?
log ( 2.7 = 0.43)
-
9.43
-
11.72
-
8.73
-
9.08
A.
9.43
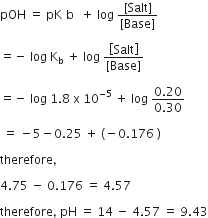
Sponsor Area
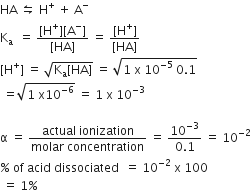
A Weak acid, HA has a Ka of 1.00 x 10-5. If 0.100 mole of this percentage of acid dissociated at equilibrium is closest to:
-
99.0%
-
1.00%
-
99.9 %
-
0.100%
B.
1.00%
An aqueous solution of which of the following compounds is the best conductor of electric current?
-
Acetic acid C2H4O2
-
Hydrochloric acid, HCl
-
Ammonia, NH3
-
Fructose, C6H12O6
B.
Hydrochloric acid, HCl
HCl is strong acid and dissociates completely. Hence, it conducts electricity best in its aqueous solution.
Base strength of 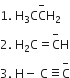
is in the order of
-
(2) > (1) > (3)
-
(3) > (2) > (1)
-
(1) > (3)> (2)
-
(1) > (2) > (3)
D.
(1) > (2) > (3)
Stronger the acid, weaker is its conjugate base.
The strength of their conjugate acids are in the order: 
Therefore, the correct order of strength of their conjugate base is: 
Buffer solutions have constant acidity and alkalinity because
-
these give unionised acid or base on reaction with added acid or alkali
-
acids and alkalies in these solutions are shielded from attack by other ions.
-
they have a large excess of H+ or OH- ions
-
they have fixed value of pH
A.
these give unionised acid or base on reaction with added acid or alkali
If a small amount of an acid or alkali is added to a buffer solution, it converts them into unionised acid or base. Thus, remains unaffected or in other words its acidity/alkalinity remains constant. e.g.,
H3O+ + A- ⇌ H2O +HA
-OH +HA → H2O +A-
If acid is added, it reacts with A- to form undissociated HA. Similarly, if base/alkali is added, O H- combines with HA to give H2O and A- and thus, maintains the acidity/alkalinity of buffer solution.
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





