Reproduction In Organisms
Sponsor Area
Archegoniophore is present in
-
Chara
-
Adiantum
-
Funaria
-
Marchantia
D.
Marchantia
In Marchantia, a bryophyte, the archegonia (female sex organs) are borne on special branches called archegoniophore or female receptacles. Each archegoniophore has rows of archegonia protected by involucre or perichaetium.
Sponsor Area
Examine the figure below and select the right option giving all the four part (A, B,C and D) correctly identified.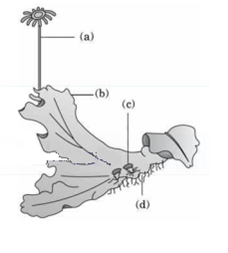
-
A
B
C
D
Archegoni Ophore
Female thallus
Gemma cup
Rhizoids
-
A
B
C
D
Archegoni
Female thallus Bud Foot -
A
B
C
D
Seta
Sporophyte Protonema Rhizods -
A
B
C
D
Antheridiophore
Male thallus Globule Roots
A.
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
Archegoni Ophore |
Female thallus |
Gemma cup |
Rhizoids |
Marchantia, a liverwort, is dioecious. The female thallus bears female sex organs called archegonia on special branches called archegoniophores. The plant's body is anchored by unicellular rhizoids.
How many different kinds of gametes will be produced by a plant having the genotype AABbCC?
-
Three
-
Four
-
Nine
-
Two
D.
Two
The types of gametes produced by a plant depend upon the number of hetrozygous pair.
Number of types of gametes = Zn
n = number of heterozygous pair
21 = 2
The gametes are - ABC and AbC.
In cloning of cattle a fertillized egg is taken out of the mother’s womb and
-
the egg is divided into 4 pairs of cells which are implanted into the womb of other cows
-
in the eight cell stage, cells are separated and cultured until small embryos are formed which are implanted into the womb of other cow
-
in the eight cell stage the individual cells are separated under electrical field for further development in culture media
-
from this upto eight identical twins can be produced
B.
in the eight cell stage, cells are separated and cultured until small embryos are formed which are implanted into the womb of other cow
In cloning of cattle a fertilized egg divides in 2, then in 4 and then in 8. This embryo is carefully removed from the womb. The embryonic cells are then separated using enzyme. Each isolated cell is kept in a nutrient medium and later implanted in the womb of a different 'host mother' cow.
In ginger vegetative propagation occurs through
-
rhizome
-
offsets
-
bulbils
-
runners
A.
rhizome
In ginger, vegetative propagation occurs through rhizome. Rhizomes are stems which grow horizontally under the ground. In ginger, the underground stems are swollen with food reserves. The terminal bud grows upward to produce the flowering shoot and the lateral buds grow out to form new plant.
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





