Breathing And Exchange Of Gases
Sponsor Area
Person with blood group AB is considered as universal recipient because he has
-
Both A and B antigens on RBC but no antibodies in the plasma
-
Both A and B antibodies in the plasma
-
No antigen or RBC and no antibody in the plasma
-
Both A and B antigens in the plasma but no antibodies
Both A and B antigens on RBC but no antibodies in the plasma
Both A and B antibodies in the plasma
No antigen or RBC and no antibody in the plasma
Both A and B antigens in the plasma but no antibodies
A.
Both A and B antigens on RBC but no antibodies in the plasma
Blood group AB is universal recipient because the person with AB blood group has both A and B antigens or RBC but no antibodies in the plasma. Other blood groups and their genotypes are
|
Blood Group |
Antigen(s) Present on the RBC |
Antibodies Present in Serum |
Genotypes |
|
A |
Antigen – A |
Anti – b |
AA/AQ |
|
B |
Antigen –B |
Anti – a |
BB/BO |
|
C |
None |
Anti – a and b |
O |
Sponsor Area
A large proportion of oxygen is left unused in the human blood even after its uptake by the body tissue. This O2
-
Raise the pCO2 of blood 75 mm of Hg.
-
Is enough to keep oxyhaemoglobin
-
helps in releasing more O2 to the epithelial tissues
-
acts as a reserve during muscular exercises
D.
acts as a reserve during muscular exercises
Our tissue is able to utilise only 25% of O2 carried by the arterial blood. The venous blood is still 75% saturated with O2. This O2 acts as a reserve during muscular exercise.
Aerobic respiratory pathway is appropriately termed
-
catabolic
-
parabolic
-
amphibolic
-
anabolic
C.
amphibolic
An amphibolic pathway is a biochemical pathway that serves both anabolic and catabolic processes. An important example of an amphibolic pathway is the Kerbs cycle, which involves both the catabolism of carbohydrates and fatty acid and the synthesis, eg alpha-ketoglutarate and oxaloacetate.
Bulk of carbon dioxide (CO2) released from body tissue into the blood is present as
-
bicarbonate in blood plasma and RBCs
-
free CO2 in blood plasma
-
70% carbamino - haemoglobin and 30% as bicarbonate
-
carbamino - haemoglobin in RBCs
A.
bicarbonate in blood plasma and RBCs
70-75% of CO2 is transported as sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) by plasma, and as potassium bicarbonate (KHCO3) by RBCs.
Figure shows schematic plan of blood circulation in human with labels A to D. Identify to label and give its function/s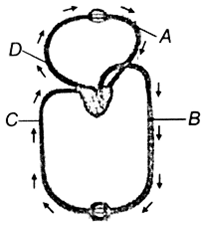
-
A - pulmonary vein - takes impure blood from body parts,pO2 = 60 mmHg
-
B - pulmonary artery - takes blood from heart to lungs, pO2 = 90 mmHg
-
C - vena cava - takes blood from body parts to right auricle, pCO2 = 45 mmHg
-
D - dorsal aorta -takes blood from heart to body parts, pO2 = 95 mmHg
C.
C - vena cava - takes blood from body parts to right auricle, pCO2 = 45 mmHg
A - pulmonary vein takes impure blood from body part, pO2 = 60 mmHg
B - Pulmonary artery - takes blood from heart to lungs, pO2 = mmHg
C- Vena cava -takes blood from body parts to right auricle, pCO2 = 45 mm Hg
D- Dorsal aorta takes blood from heart to body parts, pO2 = 95 mm Hg
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





