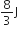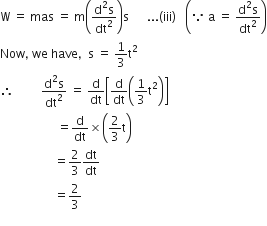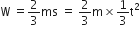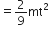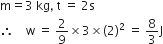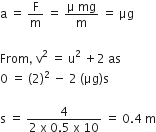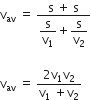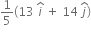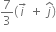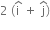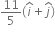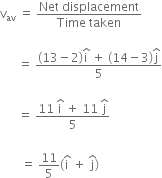A ball is dropped from a high-rise platform at t=0 starting from rest. After 6s another ball is thrown downwards from the same platform with a speed v. The two balls meet at t= 18s. What is the value of v? (take g= 10 ms-2)
-
74 ms-2
-
55 ms-1
-
40 ms-1
-
60 ms-1
A.
74 ms-2
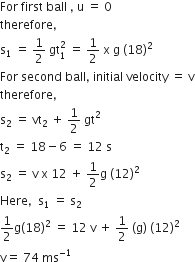






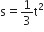 , where t is in s. Work done by the force in 2 s is:
, where t is in s. Work done by the force in 2 s is: