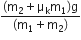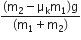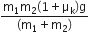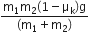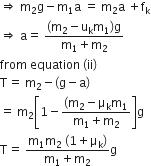300 J of work is done in sliding a 2 kg block up an inclined plane of height 10 m. Taking =10 m/s2, work done against friction is
-
200 J
-
100 J
-
Zero
-
1000 J
B.
100 J
Net work done in sliding a body up to a height h on inclined plane
= Work done against gravitational force + Work done against frictional force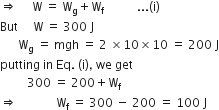






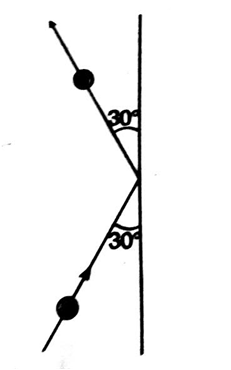
 represents the momentum of the object before the collision, and the vector
represents the momentum of the object before the collision, and the vector  that after the collision. The vector
that after the collision. The vector  represents the change in momentum of the object
represents the change in momentum of the object  .
. 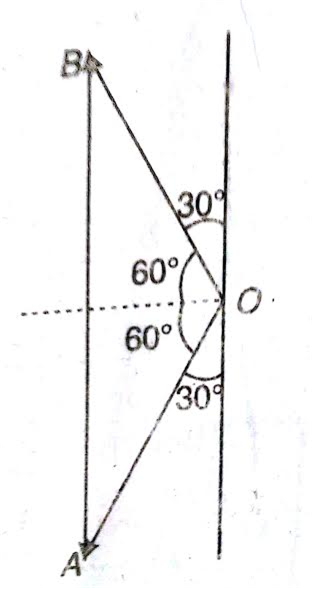
 are equal, the components of
are equal, the components of  along the wall are equal and in the same direction, while those perpendicular to the wall are equal and opposite. Thus, the change in momentum is due only to the change in direction of the perpendicular components.
along the wall are equal and in the same direction, while those perpendicular to the wall are equal and opposite. Thus, the change in momentum is due only to the change in direction of the perpendicular components.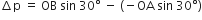

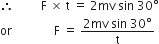
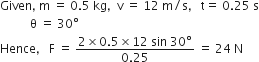
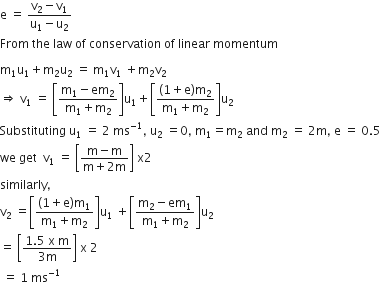
 . When the block A is sliding on the table, the tension in the string is
. When the block A is sliding on the table, the tension in the string is