A 0.1 molal aqueous solution of a weak acid is 30% ionised. if Kf for water is 1.86oC/m, the freezing point of the solution will be
-
-18oC
-
-0.54oC
-
-0.36oC
-
-0.24oC
D.
-0.24oC

A 0.1 molal aqueous solution of a weak acid is 30% ionised. if Kf for water is 1.86oC/m, the freezing point of the solution will be
-18oC
-0.54oC
-0.36oC
-0.24oC
D.
-0.24oC

A 1000C the vapour pressure of a solution of 6.5 g of a solute in 100 g water is 732 mm. If Kb = 0.52, the boiling point of this solution will be
1000C
1020C
1030C
1010C
D.
1010C
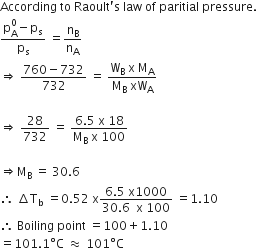
A mixture of gases contains H2 and O2 gases in the ratio of 1:4 (w/w).what is the molar ratio of the two gases in the mixture?
1:4
4:1
16:1
2:1
B.
4:1
Let the mass of H2 gas be x g and mass of O2 gas 4x g
Molar H2 : O2
mass 2 : 32
Sponsor Area
A solution containing 10 g per dm3 is urea (molecular mass = 60 g mol-1) is isotonic with a molecular mass of this non-volatile solute. The molecular mass of this of this non-volatile solute is:
250 g mol-1
300 g mol-1
350 g mol-1
200 g mol-1
B.
300 g mol-1
10 g per dm3 of urea is isotonic with 5% solution of a non-volatile solute. Hence, between this solution osmosis is not possible so, their molar concentrations are equal to each other,
Thus, molar concentration of urea solution

Sponsor Area
A solution of acetone in ethanol:
shows a negative deviation from Raoult's law
shows a positive deviation from Raoult's law
behave likea near ideal solution
obeys Raoult's law
B.
shows a positive deviation from Raoult's law
A solution ofacetone in ethanol shows a positive deviation from Raoult's law due to miscibility of these two liquids with a difference of polarity and length of the hydrocarbon chain.
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series