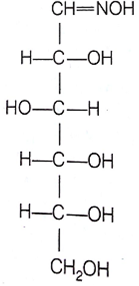
D-(+)- glucose reacts with hydroxylamine and yields an oxime. The structure of the oxime.The structure of the oxime would be
D.

Sponsor Area
D-(+)- glucose reacts with hydroxylamine and yields an oxime. The structure of the oxime.The structure of the oxime would be
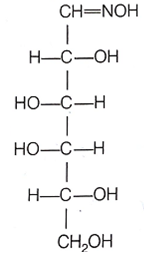
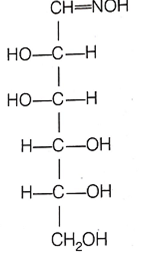
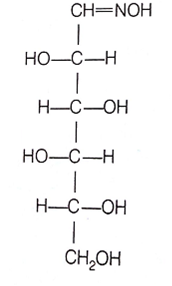

D.


Sponsor Area
Deficiency of vitamin B1 causes the disease
convulsions
beri-beri
cheilosis
sterility
B.
beri-beri
Deficiency of vitamin B1 cause beri-beri in which they occur a loss of appetite and vigour, weak heart beat etc.
During the process of digestion, the proteins present in food materials are hydrolysed in amino acids. The two enzymes involved in the process
![]()
are respectively:
amylase and maltase
diastase and lipase
pepsin and trypsin
invertase and zymase
C.
pepsin and trypsin
In the process of digestion, the proteins present in food material are hydrolysed to an amino acid. In this process two enzymes pepsin and trypsin are involved as follows:
![]()
Fructose reduces Tollen's reagent due to
asymmetric carbons
primary alcoholic group
secondary alcoholic group
enolization of fructose followed by conversion to the aldehyde by base
D.
enolization of fructose followed by conversion to the aldehyde by base
In aqueous solution, fructose is enolized and then converted into aldehyde in basic medium. All aldehydes generally reduces Tollen's reagent thus fructose also reduces Tollen's reagent.
In a protein molecule various amino acids are linked together by
peptide bond
dative bond
B.
peptide bond
Two amino acids on the protein are linked by a peptide bond. For example. Glycyllalanine is formed when carboxyl group of glycine combines with the amino group of alanine.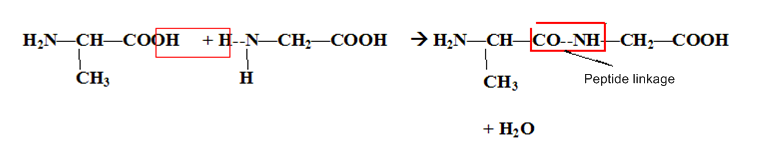
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series