Propionic acid with Br2-P yields a dibromo product. Its structure would be
-
CH2Br - CHBr -COOH
-
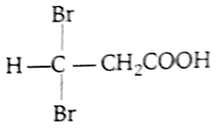
-
CH2-Br-CH2-COBr
-
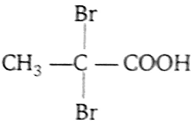
D.

Br2 in presence of P attacks on the alpha carbon atom of acid and alpha hydrogen is substituted by bromine.
This reaction is called Hell -Volhard Zelinsky (HVZ) reduction.








