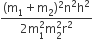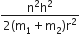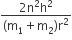System Of Particles And Rotational Motion
Sponsor Area
A ‘T’ shaped object with dimensions shown in the figure, is lying on a smooth floor. A force F is applied at the point P parallel to AB, such that the object has only the translational motion without rotation. Find the location of P with respect to C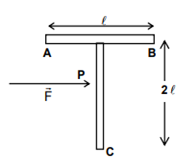
-
2
-
3
-
4
C.
4
The point P must be the centre of mass of the T-shaped object since the force F does not produce any rotational motion of the object. So, we have to find the distance of the centre of mass from the point C.
The horizontal part of the T-shaped object has length L. If the mass of the horizontal portion is ‘m’, the mass of the vertical portion of the T- shaped object is 2m since its length is 2L. For finding the centre of mass of the T shaped object, it is enough to consider two point masses m and 2m located respectively at the midpoints of the horizontal and vertical portions of the T.
Therefore, the T-shaped object reduces to two point masses m and 2m at distances 2L and L respectively from the point C. The distance ‘r’ of the centre of mass of the system from the point C is given by
r = (m1r1 + m2r2)/(m1 + m2) = (m×2L + 2m×L)/(m + 2m) = 4L/3
[ Note that we have used the equation, r = (m1r1 + m2r2)/(m1 + m2) for the position vector r of the centre of mass in terms of the position vectors r1 and r2 of the point masses m1 and m2. We could use the simple equation involving the distances from C since the points are collinear].
Sponsor Area
A bob of mass m attached to an inextensible string of length l is suspended from a vertical support. The bob rotates in a horizontal circle with an angular speed ω rad/s about the vertical. About the point of suspension
-
angular momentum is conserved
-
angular momentum changes in magnitude but not in the direction
-
angular momentum changes in direction but not in magnitude
-
angular momentum changes both in direction and magnitude
C.
angular momentum changes in direction but not in magnitude
A circular disc of radius R is removed from a bigger circular disc of radius 2R such that the circumferences of the discs coincide. The centre of mass of the new disc is α/R from the centre of the bigger disc.The value of α is
-
1/3
-
1/2
-
1/6
-
1/4
A.
1/3
In this question distance of centre of mass of new disc is αR not α/R.

A cylindrical tube, open at both ends, has a fundamental frequency, f, in the air. The tube is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air-column is now
-
m1r1:m2r2
-
m1 :m2
-
r1 :r2
-
1:1
C.
r1 :r2
As their period of revolution is same, so its angular speed is also same. Centripetal acceleration is circular path,
a= ω2r
Thus, 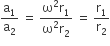
A diatomic molecule is made of two masses m1 and m2 which are separated by a distance r. If we calculate its rotational energy by applying Bohr's rule of angular momentum quantization, its energy will be given by (n is an integer)
D.
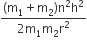
Rotational kinetic energy of the two body system rotating about their centre of mass is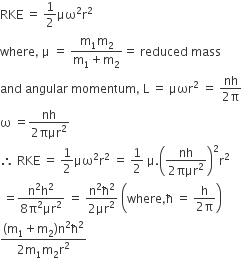
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series