Ray Optics And Optical Instruments
Sponsor Area
In an optics experiment, with the position of the object fixed, a student varies the position of a convex lens and for each position, the screen is adjusted to get a clear image of the object. A graph between the object distance u and the image distance v, from the lens, is plotted using the same scale for the two axes. A straight line passing through the origin and making an angle of 45o with the x-axis meets the experimental curve at P. The coordinates of P will be
-
(2f, 2f)
-
(f/2, f/2)
-
(f,f)
-
(4f, 4f)
A.
(2f, 2f)
It is possible when object kept at centre of curvature.
u = v
u = 2f,
v = 2f.
Sponsor Area
A car is fitted with a convex sideñview mirror of focal length 20 cm.Asecond car 2.8 m behind the first car is overtaking the first car at a relative speed of 15 m/s. The speed of the image of the second car as seen in the mirror of the first one is
-
1/15 m/s
-
10 m/s
-
15 m/s
-
1/10 m/s
A.
1/15 m/s
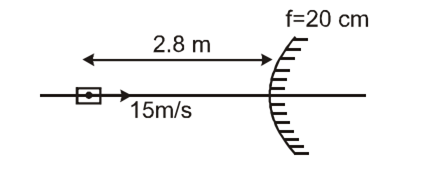
The mirror formula
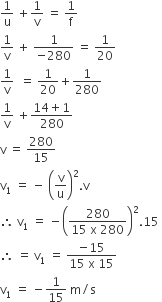
A circular loop of radius 0.3 cm lies parallel to a much bigger circular loop of radius 20 cm. The centre of the small loop is on the axis of the bigger loop. The distance between their centres is 15 cm. If a current of 2.0 A flows through the smaller loop, then the flux linked with bigger loop is
-
9.1 x 10-11 Wb
-
6 x 10-11 Wb
-
3.3 x 10-11 Wb
-
6.6 x 10-9 Wb
A.
9.1 x 10-11 Wb
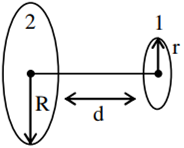
Let M12 be the coefficient of mutual induction between loops
A diverging lens with the magnitude of focal length 25 cm is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a converging lens of the magnitude of focal length 20 cm. A beam of parallel light falls on the diverging lens. The final image formed is
-
real and at a distance of 40 cm from the divergent lens
-
real and at a distance of 6 cm from the convergent lens
-
real and at a distance of 40 cm from the convergent lens
-
virtual and at a distance of 40 cm from the convergent lens
C.
real and at a distance of 40 cm from the convergent lens
As parallel beam incident on diverging lens if forms virtual image at v1 = –25 cm from the diverging lens which works as an object for the converging lens (f = 20 cm)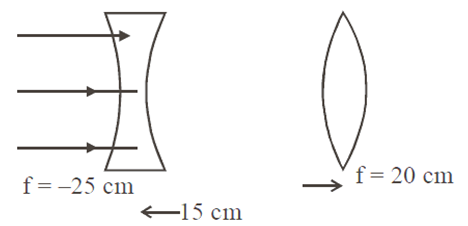
So for converging lens u = -40 cm, f = 20 cm
therefore final image
V = 40 cm from the converging lens.
A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in the air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now:
-
f/2
-
3f/4
-
2f
-
f
D.
f
For open ends, fundamental frequency f in air
we have
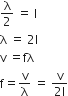
When a pipe is dipped vertically in the water, so that half of it is in water, we have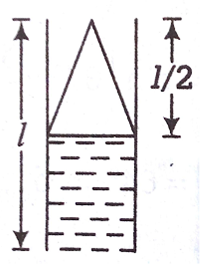
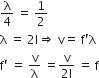
Thus, the fundamental frequency of the air column is now,
f=f'
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





