States Of Matter
Sponsor Area
'a' and 'b' are van der Waals constants for gases. Chlorine is more easily liquefied than ethane because :
-
a and b for Cl2 > a and b for C2H6
-
a and b for Cl2 < a and b for C2H6
-
a and Cl2 < a for C2H6 but b for Cl2 > b for C2H6
-
a for Cl2 > a for C2H6 but b for Cl2 < b for C2H6
D.
a for Cl2 > a for C2H6 but b for Cl2 < b for C2H6
Vander Waals, constant a is due to force of attraction and b due to the infinite size of molecules. Thus, greater the value a and smaller the value b, larger the liquefaction.
| a | b | |
| Cl2 | 6.579 L2 bar mol-2 | 0.05622 L bar mol-2 |
| C2H5 | 5.562 L2 bar mol-2 | 0.06380 L mol-1 |
Sponsor Area
An ideal gas expands in volume from 1×10-3 m3 to 1×10-2 m3 at 300 K against a constant pressure of 1×105 Nm-2. The work done is
-
-900 J
-
900 J
-
2780 J
-
-2780 J
A.
-900 J
Work done due to change in volume against constant pressure is
W = - p(V2-V1)
= - 1 x 105 Nm-2 (1 x 10-2- 1 x 10-3)m3
As the temperature is raised from 20°C to 40°C, the average kinetic energy of neon atoms changes by a factor of which of the following?
-
1/2
-
2
-
313/293
-

C.
313/293
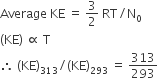
Assuming that water vapour is an ideal gas, the internal energy change(∆U) when 1 mol of water is vapourised at 1 bar pressure and 100°C, (Given: Molar enthalpy of vapourisation of water at 1 bar and 373 K = 41 kJ mol-1 and R = 8.3 J mol–1K–1 will be) –
-
4.100 kJ mol–1
-
3.7904 kJ mol–1
-
37.904 kJ mol–1
-
41.00 kJ mol–1
C.
37.904 kJ mol–1

∆ng =1−0 =1
∆H =∆U +∆ngRT
∆U =∆H −∆ngRT
= 41 – 8.3 × 10-3 × 373
= 37.9 kJ mol-1
For the gaseous state, if most probable speed is denoted by C*, average speed by C and mean square speed by C, then for a large number of molecules the ratios of these speeds are:
C.
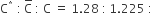
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series