Solutions
Sponsor Area
1 gram of a carbonate (M2CO3) on treatment with excess HCl produces 0.01186 mole of CO2. The molar mass of M2CO3 in g mol-1 is
-
1186
-
84.3
-
118.6
-
11.86
B.
84.3
Given chemical equation
M2CO3 +2HCl → 2MCl + H2O + CO2
1 gm 0.01186 mol
From the balanced chemical equation
1/M = 0.01186
M = 84.3 gm/mol
Sponsor Area
18 g glucose (C6H12O6 ) is added to 178.2 g water. The vapor pressure of water (in torr) for this aqueous solution is:
-
76.0
-
752.4
-
759.0
-
7.6
B.
752.4
Vapour pressure of water (p°) = 760 torr
Number of moles of glucose
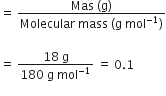
Molar mass of water = 18 g/mol
Mass of water (given) = 178.2 g
Number of moles of water
![]()
Total number of moles = (0.1 +9.9) = 10 moles
Now, the mole fraction of glucose in solution = Change in pressure with respect to initial pressure.
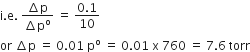
therefore, Vapour pressure of solution = (760-7.6)torr
=752.4 torr
18 g of glucose (C6H12O6) is added to 178.2 g of water. The vapour pressure of water for this aqueous solution at 100o C is
-
759.00 Torr
-
7.60 Torr
-
76.00 Torr
-
752.40 Torr
C.
76.00 Torr
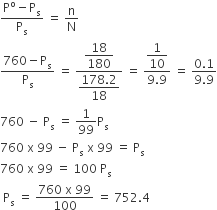
3 g of activated charcoal was added to 50 mL of acetic acid solution (0.06N) in a flask. After an hour it was filtered and the strength of the filtrate was found to be 0.042 N. The amount of acetic acid adsorbed (per gram of charcoal) is:
-
18 mg
-
36 mg
-
42 mg
-
54 mg
A.
18 mg
The initial strength of acetic acid = 0.06N
Final strength = 0.042 N
Volume given = 50 mL
there Initial m moles of CH3COOH
= 0.06 x 50 = 3
Final m moles of CH3COOH
= 0.042 x 50 = 21
therefore, m moles of CH3COOH absorbed
= 3-2.1
= 0.9 m mol
Hence, mass of CH3COOH absorbed per gram of charcoal
= 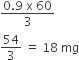
6.02×1020 molecules of urea are present in 100 ml of its solution. The concentration of urea solution is
-
0.001 M
-
0.1 M
-
0.02 M
-
0.01 M
D.
0.01 M
Avogadros number NA = 6.02 x 1023 = 1 mole
∴ 6.02 x 1020 molecules
= 0.001 mole in 100 mL (0.1 L solution)
∴ Molar concentration = mol/volume in L
=0.001/0.1
= 0.01 M
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





