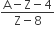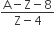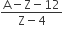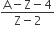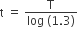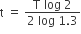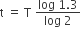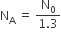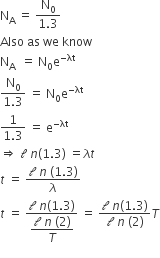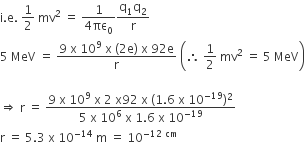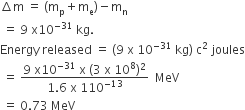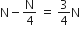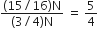A radioactive nucleus (initial mass number A and atomic number Z) emits 3 α–particles and 2 positions. The ratio of number of neutrons to that of protons in the final nucleus will be
B.
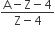
In positive beta decay a, proton is transformed into a neutron and a positron is emitted
p+ → n0 + e+
Number of neutrons initially was A-Z
Number of neutrons after decay (A-Z) -3 x 2 (due to alpha particles) + 2 x 1 (due to positive beta decay)
The number of protons will reduce by 8. so, the ratio number of neutrons to that of protons =