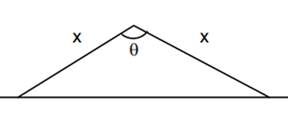
A triangular park is enclosed on two sides by a fence and on the third side by a straight river bank. The two sides having fence are of same length x. The maximum area enclosed by the park is
-
3x2/2
-
x3/8
-
x2/2
-
πx2
C.
x2/2
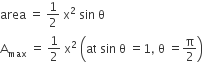
Sponsor Area
A triangular park is enclosed on two sides by a fence and on the third side by a straight river bank. The two sides having fence are of same length x. The maximum area enclosed by the park is
3x2/2
x3/8
x2/2
πx2
C.
x2/2

Sponsor Area
If (a, a2 ) falls inside the angle made by the lines y =x/2, x >0 and y = 3x, x > 0, then a belongs to
(0,1/2)
(3, ∞)
(1/2, 3)
(-3, -1/2)
C.
(1/2, 3)
If PS is the median of the triangle with vertices P(2,1), Q(6,-1) and R (7,3), then equation of the line passing through (1,-1) and parallel to PS is
4x-7y - 11 =0
2x+9y+7=0
4x+7y+3 = 0
2x-9y-11 =0
B.
2x+9y+7=0
Coordinate of S = 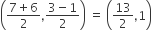
[∵ S is mid-point of line QR]
A slope of the line PS is -2/9.
Required equation passes through (1,-1) and parallel to PS is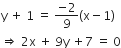
Let a,b,c and d be non-zero numbers. If the point of intersection of the lines 4ax +2ay +c= 0 and 5bx +2by +d = 0 lies in the fourth quadrant and is equidistant from the two axes, then
2bc-3ad =0
2bc+3ad =0
2ad-3bc =0
3bc+2ad=0
C.
2ad-3bc =0
Let coordinate of the intersection point in the fourth quadrant be (α, -α) lies on both lines 4ax +2ay +c =0 and 5bx +2by +d =0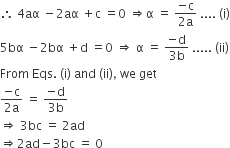
The angle between the lines whose direction cosines satisfy the equations l +m+n=0 and l2 = m2+n2 is
π/3
π/4
π/6
π/2
A.
π/3
We know that angle between two lines is 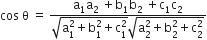
l +m +n= 0
⇒ l = - (m+n)
⇒ (m+n)2 = l2
⇒ m2 +n2 +2mn = m2 +n2
[∵ l2 = m2 +n2, given]
⇒ 2mn = 0
when m = 0 ⇒ l =-n
Hence, (l, m, n) is (1,0-1)
When n =0, then l =-m
Hence, (l,m,n) is (1,0-1)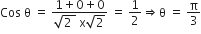
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series