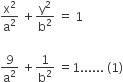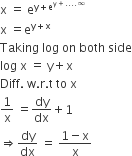A spherical balloon is filled with 4500π cubic meters of helium gas. If a leak in the balloon causes the gas to escape at the rate of 72π cubic meters per minute, then the rate (in meters per minute) at which the radius of the balloon decreases 49 minutes after the leakage began is
-
9/7
-
7/9
-
2/9
-
9/2
C.
2/9
Volume of balloon is,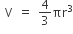
After 49 minutes volume = 4500π – 49 (72π) = 972π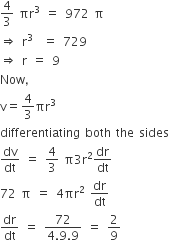






 is
is