The photon of hard gamma radiation knocks a proton out of 2412Mg nucleus to form
-
the isotope of parent nucleus
-
the isobar of parent nucleus
-
the nuclide

-
the isobar of

C.
the nuclide ![]()
The photon of hard gamma radiation knocks a proton out of 2412Mg nucleus to form
the isotope of parent nucleus
the isobar of parent nucleus
the nuclide ![]()
the isobar of ![]()
C.
the nuclide ![]()
The rate equation for the reaction 2A + B → C is found to be: rate k[A][B]. The correct statement in relation to this reaction is that the
unit of K must be s-1
values of k is independent of the initial concentration of A and B
rate of formation of C is twice the rate of disappearance of A
t1/2 is a constant
B.
values of k is independent of the initial concentration of A and B
values of k is independent of the initial concentration of A and B
Sponsor Area
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10ºC rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50ºC, the rate of the reaction increases by about
10 times
24 times
32 times
64 times
C.
32 times
For every 10o C rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. Thus, temperature coefficient of the reaction = 2 when temperature is increased by 50o rate becomes

Sponsor Area
The rate of a reaction doubles when its temperature changes from 300K to 310K. Activation energy of such a reaction will be (R = 8.314 JK–1 mol–1 and log 2 = 0.301)
53.6 kJ mol-1
48.6 kJ mol-1
58.5 kJ mol-1
60.5 kJ mol-1
A.
53.6 kJ mol-1
By using Arrhenius equation,
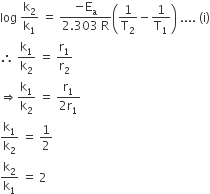
Given, T2 = 310; T1 = 300K
On putting values in Eq (i), we get
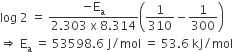
The resistance of 0.2 M solution of an electrolyte is 50 Ω. The specific conductance of the solution of 0.5 M solution of the same electrolyte is 1.4 S m-1 and resistance of the same solution of the same electrolyte is 280 Ω. The molar conductivity of 0.5 M solution of the electrolyte in Sm-2 mol-1 is
5 x 10-4
5 x 10-3
5 x 103
5 x 102
A.
5 x 10-4
For first solution,
k = 1.4 Sm-1, R =50 Ω , M =0.2
specific conductance

Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series