Ray Optics And Optical Instruments
Sponsor Area
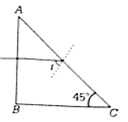
A beam of light consisting of red, green and blue colours is incident on a right-angled prism. The refractive index of the material of the prism for the above red, green and blue wavelength are 1.39, 1.44 nd 1.47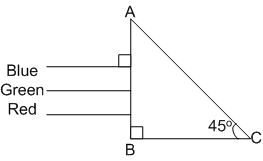
The Prism will
-
separate the blue colour part from the red and green colours
-
separate all the three colours from one another
-
not separate the three colours at all
-
separate the red colour part from the green and blue colours
D.
separate the red colour part from the green and blue colours
For refractive index of a index.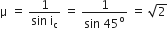
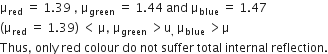
Sponsor Area
A beam of light from a source L is incident normally on a plane mirror fixed at a certain distance x from the source. The beam is reflected back as a spot on a scale placed just above the source L. When the mirror is rotated through a small angle θ, the spot of the light is found to move through a distance y on the scale. The angle θ is given by
-
y/2x
-
y/x
-
2y/x
-
y/x
A.
y/2x
When the mirror is rotated by θ angle reflected ray will be rotated by 2θ.
y/x = 2θ
θ = y/2x
A biconvex lens has a radius of curvature of magnitude 20 cm. Which one of the following options describes best the image formed on an object of height 2 cm placed 30 cm from the lens?
-
Virtual, upright, height = 0.5 cm
-
Real, invented, height = 4 cm
-
Real, inverted, height = 1 cm
-
Virtual, upright, height = 1 cm
B.
Real, invented, height = 4 cm
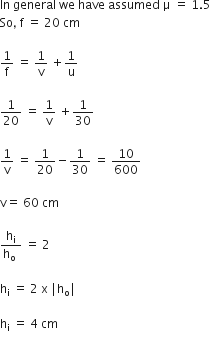
Here, image is real, inverted, magnified field and height of image is 4 cm
A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must be equal
-
f1 +f2
-
-f1 +f2
-
2f1+f2
-
-2f1 +f2
C.
2f1+f2
d= 2f1 +f2
A conversing beam of rays is incident on a diverging lens. Having passed though the lens the rays intersect at a point 15 cm from the lens on the opposite side. If the lens is removed the point where the rays meets will moves 5 cm closer to the lens. The focal length of the lens is
-
-10 cm
-
20 cm
-
-30 cm
-
5 cm
C.
-30 cm
Given u = 10 cm, v = 15 cm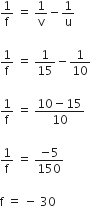
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





