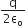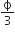Electric Charges And Fields
Sponsor Area
A beam of cathode rays is subjected to crossed Electric (E) and magnetic field (B). The fields are adjusted such that the beam is not deflected. The specific charge of the cathode rays is given by
(Where V is the potential difference between cathode and anode)
-
B2/2VE2
-
2VB2/E2
-
2VE2/B2
-
2E2/2VB2
D.
2E2/2VB2
As the electron beam is not deflected,
then
Fm = Fe
Or BeV = Ee
Or v= E/B .... (i)
As the electron moves from the cathode to anode, its potential energy at the cathode appears as its kinetic energy at the anode. If V is the potential difference between the anode and cathode, then potential energy of the electron at cathode = eV. Also, the kinetic energy of the electron at anode = mv2 /2. According to law of conservation of energy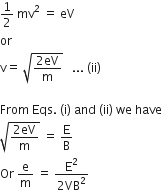
Sponsor Area
A charge Q is enclosed by a Gaussian spherical surface of radius R. If the radius is doubled, then the outward electric flux will
-
be reduced to half
-
remain the same
-
be doubled
-
increase four times
B.
remain the same

A conducting sphere of radius R is given a charge Q. The electric potential and the electric field at the centre of the sphere respectively are:
-
zero and

-

-
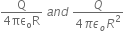
-
Both are zero
B.


Electric field inside, Einside = 0
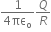
A hollow cylinder has to charge q coloumb within it. Φ is the electric flux in a unit of voltmeter associated with the curved surface B, the flux linked with the plane surface A in a unit of voltmeter will be:
A.
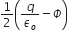
Apply Gauss's law to calculate the charge associated with plane surface A.
Gauss's law states that the the net electric flux through any clsoed surface is equal to the net charge inside the surface divided by εo.That is 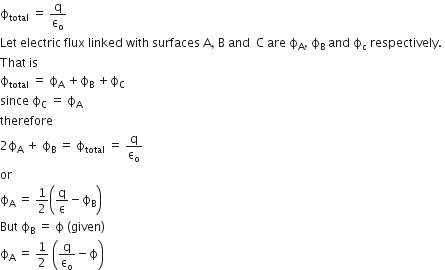
A square surface of side L m is in the plane of the paper. A uniform electric field 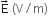 , also in the plane of the paper, is limited only to the lower half of the square surface, (see figure). The electric flux in SI units associated with the surface is
, also in the plane of the paper, is limited only to the lower half of the square surface, (see figure). The electric flux in SI units associated with the surface is
-
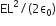
-

-
zero
-

C.
zero
Electric flux  is a measure of the number of field lines crossing a surface. The number of field lines passing through unit area (N/S) will be proportional to the electric field, or,
is a measure of the number of field lines crossing a surface. The number of field lines passing through unit area (N/S) will be proportional to the electric field, or,
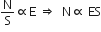
The quantity ES is the electric flux through surface S.
As we have seen in the problem that, lines of force that enter the closed surface leave the surface immediately, so no electric flux is bound to the system. Hence, electric flux is zero.
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series