Dimensions of resistance in an electrical circuit, in terms of the dimension of mass M, of length L, of time T and of current I, would be:
-
[ML2T-3I-1]
-
[ML2T-2]
-
[ML2T-1I-1]
-
[ML2T-3I-2]
D.
[ML2T-3I-2]
Resistance 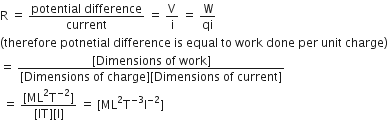
Sponsor Area
Dimensions of resistance in an electrical circuit, in terms of the dimension of mass M, of length L, of time T and of current I, would be:
[ML2T-3I-1]
[ML2T-2]
[ML2T-1I-1]
[ML2T-3I-2]
D.
[ML2T-3I-2]
Resistance 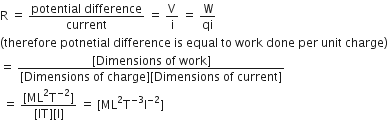
Sponsor Area
If energy (E), velocity (v) and time (T) are chosen as the fundamental quantities, the dimensional formula of surface tension will be
[Ev-2T-1]
[Ev-1T-2]
[Ev-2T-2]
[E-2v-1T-3]
C.
[Ev-2T-2]

If force (F), velocity (v) and time (T) are taken as fundamental units, then the dimensions of mass are
[FvT-1]
[FvT-2]
[Fv-1T-1]
[Fv-1T]
D.
[Fv-1T]
We know that,
F = ma
That is,
F = mv/t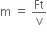
So, 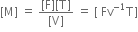
If the dimensions of a physical quantity are given by Ma Lb Tc, the physical quantity will be
pressure if a = 1, b = -1, c= 2
velocity if a = 1, b = 1, c = -2
acceleration if a = 1, b = 1, c =-2
force if a = 0, b = -1, c =- 2
A.
pressure if a = 1, b = -1, c= 2
Dimensions of velocity = [ M0L1T-1]
Here, a = 0, b =1, c = -1
Dimension of acceleration = [ M0L1T-2]
Dimension of force = [ M1L1T-2]
Dimension of pressure = [M1L-1T-2
The physical quantity is pressure.
If the error in the measurement of radius of sphere is 2%, then the error in the determination of volume of the sphere will be
4%
6%
8%
2%
B.
6%

Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series