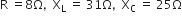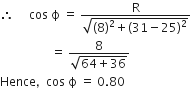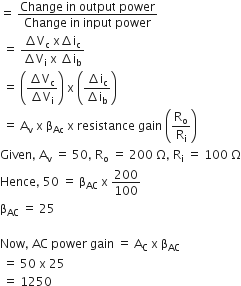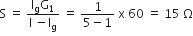A 220 V input is supplied to a transformer. The output circuit draws a current 2.0 A at 440 V. If the efficiency of the transformer is 80%, the current drawn by the primary windings of the transformer is
-
3.6 A
-
2.8 A
-
2.5 A
-
5.0 A
D.
5.0 A
Efficiency is defined as the ratio of output power and input power
i.e. 






 is the ratio of resistance and impedance of a.c. circuit.
is the ratio of resistance and impedance of a.c. circuit.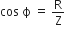 ...(i)
...(i)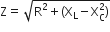 ...(ii)
...(ii)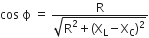 ...(iii)
...(iii)